Introduction
Stellar is a fully accessible network designed for asset release and transactions. Also known as Stellar Lumens, it is an open-source, decentralized system allowing cross-border payments between any two currencies and low-cost digital currency to fiat currency transfers. Stellar Blockchain’s founder, Jed McCaleb, is also a Ripple co-founder. It is faster, cheaper, and more efficient than other blockchain-based financial access and inclusion systems.
Stellar Lumens (XLM) is the cryptocurrency the Stellar platform uses to transact between countries. The Stellar Consensus Protocol provides access to the exchange of money and tokens through a decentralized network that connects symmetric servers (nodes) in the Stellar network. Anybody can bring a Stellar Core verification node to life with the help of the backbone of the Stellar’s network, which is the Stellar Core.
The Stellar core is in control of all the functionalities of the universe, including transaction verification. Through the Stellar Consensus Protocol, an algorithm for transaction verification over the Stellar network, the Stellar core is responsible for transaction verification. Trusted nodes that verify transactions are in control of the Stellar core.
What is Stellar Lumens?
The Stellar Network is open to all manners of money and cryptocurrency; it sure does have a currency named Lumens. Generally, it is Lumens that pay for the mode of paying transaction fees on the Stellar Network. It also facilitates fast exchange trades for Stellar users by being an intermediate currency.
Money sent over Stellar is automatically converted to Lumens and converted to the desired coin automatically by a built-in protocol. For instance, Stellar will convert a U.S. dollar payment to lumens for a recipient in Mexico, who will then get paid in pesos. A complete conversion takes seconds to send and receive money quickly from anywhere worldwide.
History of Steller
Stellar is the brainchild of Jed McCaleb and Joyce Kim, who founded it in 2014. Before Stellar, McCaleb had worked on the Ripple payment protocol and co-founded the first Bitcoin exchange, Mt. Gox. It aimed at creating an open-source, decentralized cross-border payment platform using blockchain technology that may be friendlier and more effective. In 2015, they created the genesis block in Stellar, but with 100 billion Lumen (XLM).
In 2016, Stellar disclosed a partnership with IBM to expand its use of blockchain technology by powering a new settlement system for major banks. This relationship included the IBM Blockchain World Wire – the cross-border payment platform focused on being used on the Stellar network.
In the last few years, partners and users of the Stellar network have increased. To promote access to finance and financial inclusion, Stellar Lumens (XLM) paved the way for launching Airdrops in partnership with Deloitte, Stronghold, and Tempo. Stellar network is one of the largest decentralized platforms of users, partners, and developers, which allows cross-border payment. In other words, it allows for cross-border money transfers, but other than that, it provides financial inclusion and access to the world for their people.
How does the Stellar blockchain operate?
Like any other blockchain platform, the Stellar network adds transactions to the shared and distributed public ledger. Stellar uses a “Stellar Consensus Protocol,” an FBA (Federated Byzantine Agreement) consensus algorithm. SCP easily enables quick, low-cost transactions because all network participants reach a consensus on the transaction’s validity in a few seconds.
Each participant (also called a node) that helps add the transactions to the world ledger chooses its mini-network of other trusted participants. Such a mini-network is called a Quorum Slice. Using those Quorum Slices, the Stellar network can quickly search within these slices and look for an agreement on valid transactions to add them to the ledger.
Important features of Stellar blockchain
Now that we’ve covered the basics of Stellar blockchain let’s go over some of the most important features:
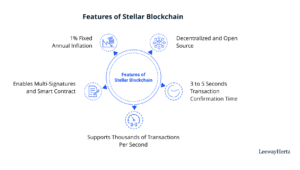
- The Stellar database is decentralized and open-source, two key characteristics of a real blockchain technology.
- The consensus process enables a transaction confirmation time of 3 to 5 seconds.
- It can process thousands of transactions per second.
- It supports multiple signatures and smart contracts.
- It has a 1% fixed yearly inflation rate.
Decoding Stellar: The Payment Revolution
Let us use an example to understand better how the Stellar payment system works.
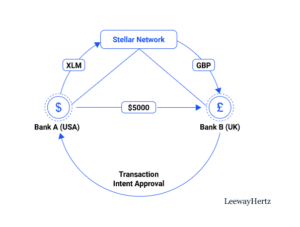
Janet stays in the USA, and Keith lives in the U.K. Janet wants to send $5000 to Keith for a cross-border business transaction, which converts to Pound Sterling (GBP). Because Janet has an account with Bank A based in the USA and Keith with Bank B based in the U.K., these banks are connected to the Stellar network as “Anchors.” Janet transfers USD 5000 to Keith. Within seconds, Bank B receives the transaction intent and determines if Keith is compliant.
When Bank A gets approval from Bank B, the deduction should be instantaneously made from Janet’s account. Next, the USD is remitted into Bank A’s pool account and transferred as XLM into the Stellar network. It looks through the Stellar network to find the best exchange rate for converting XLM to GBP. The money is then remitted into the base account of Bank B and, after that, credited to Keith’s account.
Stellar blockchain use cases
Cross-border payments
Stellar has fast, secure, and cheap transactions; thus, it is ideal for cross-border payments. Lumens (XLM) is a real-time currency bridge for fast currency conversions, sending and receiving money worldwide with your preferred currencies.
Transfers of funds
Through Stellar, sending money from one country to another and processing remittances takes place. People and families who need to send money to their relatives or loved ones abroad will benefit from this, as transaction costs are very cheap, and transactions are completed in just a minute.
Small-scale finance
Stellar positions itself as a financial service for underbanked and unbanked populations. It supports smart contracts that are available to automate complex financial transactions and also supports low-cost transactions.
Supply chain management
Some supply chains that may benefit from Stellar include suppliers, manufacturers, and distributors. Therefore, smart contracts provided by Stellar will allow these particular supply chains to automate most of the transactions over the network, such as purchase orders and invoices.
Tokenization
The Stellar network can tokenize assets, from equities and real estate to commodities, for trading. This allows quick, secured, and low-cost exchange from transferring the ownership of assets to opening up new investment possibilities and financial inclusion opportunities.
Pros & Cons of Stellar blockchain
Pros
- Transactions are quick and efficient.
- Stellar supports smart contracts.
- Easy cross-currency conversions and an affordable option for international payments
- A more secure, censorship-resistant, and meddle-free system
Cons
- Limited scalability
- Fewer use cases at present
- Certain regions or currencies may still limit the platform’s liquidity.
- Centralizations risks
How Stellar Safeguards the Integrity of Its Financial Network
Mechanistically, the consensus of Stellar works basically on the Federated Byzantine Agreement (FBA). FBA derives its operational efficiency from quorum slices each node makes. Then, it uses consensus to reach system-level quorums, just as independent networks’ peering and transit decisions combine to form the Internet. Similarly, quorum slices bind the Stellar network together.
In the FBA system,
- Mini-networks divide participants.
- Each node in such mini-networks understands its critical players.
- When a deal begins, a node waits for most participants in its mini-network to agree before accepting the transaction as settled.
- Similarly, the other parties do not consent to the transaction unless the crucial members agree.
- Once sufficient network participants approve a transaction, a hacker or attacker cannot reverse it.
- Only then can any participant consider the transaction completed.
In this way, FBA consensus enforces the financial security and integrity that runs on the Stellar network. It ensures that SCP is free from blocked states (consensus is no longer achievable) as long as the failures of the participants do not make the trust dependencies impossible to satisfy.
What are some business applications of the Stellar blockchain?
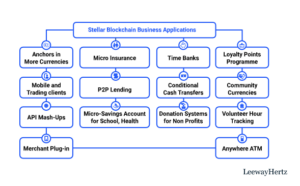
Stellar goes beyond financial markets into the safe execution of many of their vital functions by organizations. Bearing in mind the varied nature of the Stellar blockchain feature, the platform opens many opportunities and possible applications. Here are some:
- Anchors in more currencies
- Mobile and trading clients
- API Mashups
- Merchant plugin
- Micro savings account for school, health, insurance
- Microinsurance
- P2P lending
- Conditional cash transfers
- Donation systems for nonprofits
- Loyalty points programs
- Community currencies
- Time banks
- Volunteer hour tracking
- Anywhere ATM or human ATM mobile apps
Securing the Stellar Blockchain: A Deep Dive into its Security Measures
Stellar is a decentralized public ledger like most other blockchain networks. The Stellar network keeps data so private that it can rarely be prone to hacking. In such a platform in Stellar, anyone can join it as a certified server, making it decentralized and secure.
The project also added transaction fees to any attempt, which became free from the main hassle of several negligible blockchain applications. Its consensus is something of colossal importance in a decentralized payment system. By verifying and approving transactions, the many special nodes (computers) reduce dependency on a single constrained and centralized location that would guarantee all ledgers have the same state.
Thus, every node should be updating the ledger in the same manner. Every business or individual can run nodes. Consensus forms the basis of security within the blockchain, preventing dual attacks. This thus means nodes can agree upon the ledger securely.
Conclusion
The Stellar architecture accords the value of a valuable global exchange network. Stellar can host thousands of currency and token exchanges, which enable an individual to have the capability to exchange the cryptos for fiat or vice versa. The exchange is simple, and it is quick in Stellar.
Stellar is designed to allow users to have powers far from their local economies and transact with a larger pool from the global marketplace. It can support any asset, and transactions are almost free, hence desirable for micropayments.
Stellar’s blockchain technology seamlessly links financial infrastructures worldwide, offering interoperability for any form and value. It increases access and inclusion and simultaneously assures us of creating a world where access to equity is not a right but a privilege.








