Introduction
Avalanche (AVAX) is a smart-contract-powered, next-generation blockchain often considered an Ethereum competitor. The Avalanche blockchain and platform for hosting decentralized applications (DApps) and nonfungible tokens (NFTs) are efficient and fast, and the Avalanche ecosystem and its native. AVAX cryptocurrency has seen notable interest from developers and investors.
Avalanche Platform Overview
Avalanche (AVAX) is quite a platform with similar competitors to others, apart from Ethereum, such as Cardano or Solana. It poses itself as a solution to the current problem of blockchain technology in obtaining an effective fusion of speed, scalability, security, decentralization, and interoperability.
Avalanche is an ecosystem that facilitates the development of DApps, token creation, and release of games based on the blockchain. Avalanche enables projects to build customized, interoperable, and independent chains, bringing bridges for compatibility with Ethereum and other chains. The project aims to prove that its network can host transactions at lightning speed at scale.
AVAX is the native coin of Avalanche. Later, it will find applications for many more use cases, such as paying for network transactions, participating in governance, and staking. AVAX’s market share increased 275% in 2023 and crossed the $1 billion threshold of total transactions processed on the network.
The Evolution of Avalanche: A Concise History
One year later, in May 2018, the “Team Rocket,” a group of developers, published an article about the Avalanche protocol. In 2019, the Turkish-American computer scientist Emin Gün Sirer started Ava Labs to work on Avalanche.
As of 2020, reports suggested that the project had drawn $42 million at an initial coin offering (ICO) and, by 2021, had drawn another $230 million via venture funding. Avalanche’s most prominent investors include such funds as Polychain and Three Arrows Capital. The launch of the mainnet of the cryptocurrency ecosystem occurred in September 2020.
Understanding Avalanche’s Functionality
Avalanche embarks on a journey to solve all the problems blockchain technology faces using three novel features. There is an alternative proof-of-stake (PoS) consensus mechanism and use of subnetworks. Instead of a single chain, the Avalanche mainnet comprises three major blockchains.
Consensus
The Avalanche consensus is based on the classic Proof of Stake (PoS) model. It transforms each validation node into an independent entity that votes on accepting or rejecting new transactions. Then, the consensus mechanism deploys “repeated random subsampling” so that a node keeps selecting small subsets of other validators to decide upon until the network attains some threshold of confidence in the transaction.
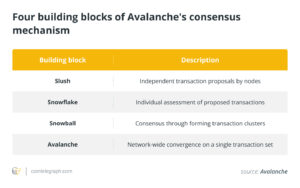
In this light, the consensus protocol of Avalanche is implemented in a scalable way yet with very small possible fault tolerance, which gives rise to a great challenge. Avalanche’s consensus also works with relatively low energy consumption compared to many other chains. The node activates to cast votes on any existing transactions when needed.
Subnetworks
Avalanche empowers developers to set up their custom blockchains, and they determine the consensus rules. Consensus for the autonomous chains is done using groups of nodes known as subnetworks or subnets to validate sets of blockchains. Subnetworks also take part in the validation on the Avalanche mainnet. It is indeed kindred and comparable to a suite of other blockchain scaling solutions, say, Polkadot’s parachains and Ethereum’s consensus-layer upgrade.
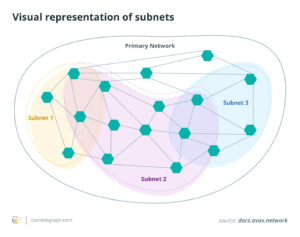
Three layer-1 built-in blockchains
The three blockchains underpinning the Avalanche platform are as follows: the Exchange Chain (X-Chain) that deals with asset issuance and transfers, including the AVAX token; the Contract Chain (C-Chain) on which Avalanche smart contracts are issued and transferred; and the Platform Chain (P-Chain) that coordinates validators and subnets.
Hence, the tokens circulate between the three chains, providing network functionality. With the three chains, the Avalanche protocol becomes a layer-1 solution rather than a layer-2 solution based on the rollup mechanism. It handles transaction validation off-chain while reaching higher transaction processing speeds.
Cross-chain functionality in Avalanche
C-Chain refers to the Avalanche Contract Chain (C-Chain). Therefore, it is an EVM-compatible platform with a chain offered for cross-operability of the projects and tokens built in the Avalanche platform. Like Ethereum, the platform uses Solidity for its smart contracts with various cross-chain bridges.
Avalanche network scalability
The Avalanche proprietary consensus mechanism is integrated with three layer-1 chains, ensuring this blockchain’s required scalability and speed. At the same time, Avalanche uses a directed acyclic graph (DAG) structure for its X-Chain, which handles token transactions, is also non-linear and, in turn, faster.
Avalanche states that it can process 6,500 transactions per second (TPS). In the meantime, Ethereum processes around 15 TPS, but with all the updates, soon it promises a significantly higher speed of TPS.
Governance
Holders of AVAX can participate in network governance, and any network node can issue a governance proposal. Avalanche uses on-chain voting for critical network parameters, such as staking amounts and times, minting rate, and transaction fee amount. It doesn’t use voting for all decisions, making it only partly decentralized.
AVAX staking mechanisms and liquidity pools
AVAX holders can stake their coins to validate transactions on the network in return for newly minted AVAX coins. Validator rewards are based on proof of uptime and proof of correctness.
Network validators don’t receive Avalanche transaction fees; fees are burned to increase AVAX’s scarcity. Avalanche is gaining a reputation for its healthy validator incentives, having paid over $275 million in AVAX to well over 1,000 validators for the network in 2023.
AVAX tokenomics
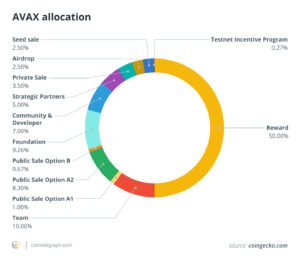
There is a capped supply of 720 million AVAX tokens. Half of these tokens were created and circulated at the mainnet launch in 2020. 10% went to the Avalanche team, 9.26% was handed over to the foundation, and 5% was allocated to strategic partners, with the rest allocated to the recipients of ICO and other places of deployment. The remaining supply is continuously minted as staking rewards.
Avalanche C-Chain applications
The Avalanche C-Chain hosts developers’ DApps, decentralized finance (DeFi) applications, nonfungible tokens (NFTs), and games. Some projects include decentralized exchange Trader Joe and WooFi, a prediction market GMX, and a cross-chain messaging system Synapse.
There is also Stargate Finance’s omnichannel project, which adds support for Avalanche and might give the platform further traction in 2024. Compared to 500+ DApps on Avalanche, approximately 5,000 DApps appear on Ethereum and BNB Smart Chain.
Avalanche ecosystem development
Key Technological Advancements
The Avalanche ecosystem is further expanding, while critical technologies like HyperSDK and Avalanche Warp Messaging (AWM) to use elastic subnets’ potential remain on the agenda. The HyperSDK aims to enhance throughput, while AWM focuses on improving interoperability. This has further propelled the adoption of the Avalanche network.
Strategic Investments and Partnerships
Ecosystem-supporting Colony Lab has committed to a $10 million AVAX investment in November 2023 to support network growth. The investment aims to fund the development of validators to support the Colony Avalanche Index (CAI) within the network, an index token that yields.
Indeed, this is on top of the recent news of Avalanche signing up partnerships with leading ecosystem participants, like Amazon Web Services and Tencent Cloud, yet again signaling the growing interest from the mainstream. Recently, the platform also did a demo proof-of-concept with JPMorgan and Apollo.
Growing Adoption and Usage
On the positive side, the recent launch of Bitcoin Ordinals, which followed Bitcoin itself, achieved 100 million inscriptions by June 2023 while also upholding the BRC-20 standard. Notably, in December 2023, for example, in five days, Avalanche users paid more than $4 million in transaction fees, mostly for creating and transferring tokens and NFTs through inscriptions.
How To Buy AVAX?
Most top crypto exchanges allow one to use the AVAX trading pair, meaning one can buy AVAX tokens from them. After that, one should open an online account with the chosen platform, and the purchase should be made, or a wallet should be connected to store the tokens. Since currencies get hacked much more than your wallet, it’s usually best to keep your tokens in one of the two—hardware or software—wallets.
The next step would be buying the token after a successful wallet connection. It is easy to place the order because the client only needs to specify a market or limit order. The latter ensures that tokens are available at the stipulated price. A limit order can be canceled anytime before the order reaches completion.
Top Avalanche Apps by Category
The top Avalanche apps (based on monthly users) available on the platform are as follows:
- Lydia Finance (LYD) – 9.2K.
- Aave (AAVE) – 12.12K.
- Snowbank (SB) – 19.48K.
- Pangolin Exchange (PNG) – 59.01K.
- Trader Joe (JOE) – 373.31K.
Pros & Cons of Avalanche
Let’s go into what we like and dislike about Avalanche:
Pros
- Fast transaction processing times
- Reward structure incentivizes participation
- Capable of supporting many blockchain-based projects
Cons
- Stiff competition from platforms like Ethereum
- Avalanche validators must stake 2,000 AVAX tokens
- Malicious or careless validators are never penalized by losing their AVAX
Avalanche’s Evolution: Looking Ahead
Between November 2023 and January 2024, the price of AVAX surged from $11.32 to a high of over $48 before retracing to $32, levels not seen since 2022. This increase could have been motivated by the market recovery of cryptocurrencies, among other factors.
Still, experts and investors are reasonably bullish about the AVAX coin and Avalanche as a layer-1 blockchain. Avalanche is catching up well in popularity due to its scalability and the ability to increase throughput. It also boasts an entirely new consensus mechanism, including strong security, and offers a flexible and customizable architecture for developers building DApps.
The blockchain of Avalanche is faster and cheaper than Ethereum’s. However, Ethereum is generally considered more decentralized and has a greater foothold in the market. With the biggest ecosystem of developers and DApps, plus proven security, Ethereum becomes the default option for smart contract-powered development. Cryptocurrency believers closely watch newer blockchains like Avalanche, Cardano, and Solana. They are eager to see which will achieve the most adoption.
Conclusion
Avalanche (AVAX) is a cryptocurrency that provides open doors for those searching for an equivalent of Ethereum, marked with high speed and scalability. The smart contracts platform presented by Avalanche supports two types of autonomous chains: decentralized applications and autonomous blockchains.








